Taurine is one of my favorite prescriptions for perimenopause, menopause, sleep, mood, insulin resistance, and migraine prevention.
Taurine is an amino acid, but unlike most amino acids, it doesn’t build protein. Instead, taurine has directly beneficial effects on the liver, brain, mitochondria, immune system, and nervous system. Taurine is so important that it makes up about 0.1 percent of total body weight.
Taurine is classified as semi-essential (or conditionally essential) because it can be made from methionine and cysteine. However, the rate of taurine synthesis is very low in humans, so for optimal health, taurine must also be ingested from animal foods such as meat, dairy, and fish. A standard omnivore diet provides about 400 mg of taurine, and there’s no taurine in plant foods.
👉🏽 Tip: Dietary or supplementary taurine is even more important for women because estrogen slows the biosynthesis of taurine.
Benefits of taurine for women’s health
Calms the brain and soothes anxiety
Taurine is a calming neurotransmitter similar in structure to glycine and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), two important calming neurotransmitters.
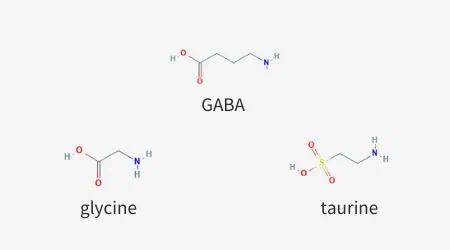
By interacting with GABA receptors, taurine helps to support beneficial “GABAergic” tone or overall GABA activity, thereby improving sleep, preventing migraines, and relieving premenstrual and perimenopausal mood symptoms. And if you’re wondering why taurine is in energy drinks, it’s included to calm the nervous system and mitigate the stimulating effects of caffeine.
👉🏽Tip: Taurine’s benefits for GABA and insulin make it particularly helpful for the hot flashes of perimenopause and menopause.
Improves insulin sensitivity and metabolic health
Taurine improves healthy insulin sensitivity by supporting mitochondria and preventing the harmful overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Together with magnesium, taurine can reduce inflammation, suppress appetite, and prevent obesity.
Supports healthy estrogen metabolism or detoxification
By supporting the healthy formation of bile acids, taurine can prevent gallstones and promote the healthy detoxification of estrogen through the liver and bowel.
May slow aging
By reducing oxidative stress and preserving mitochondrial function, taurine has been found to improve biomarkers associated with aging in humans and slow aging in animals. “Whatever we checked,” said one researcher, “taurine-supplemented animals were healthier and appeared younger than controls. Taurine made them live healthier and longer lives because it was affecting all the major hallmarks of aging.”
Builds muscle and bone
Finally, by supporting healthy muscles, taurine can help to prevent osteoporosis. That’s because the biology of bone and muscle is tightly interconnected.
How to supplement with taurine
The therapeutic dose of taurine is 500 to 3000 mg and works best when taken with magnesium, another important nutrient for mood, mitochondria, and insulin sensitivity. I usually prescribe a magnesium glycinate powder with 3000 mg of taurine. Magnesium taurate (a magnesium salt of taurine) is another option.
Is taurine safe with a sulfur allergy?
A “sulfur allergy” is usually an allergy to sulfonamides (sulfa drugs) or a sensitivity to sulfites, common in processed foods and wine. It’s not possible to have an allergy to the element sulfur, although some people can develop symptoms from a reduced ability to clear or detoxify sulfur-containing compounds.
For more about taurine, see my book Hormone repair manual: every woman’s guide to healthy hormones after 40.
